Peroxymonosulfuric acid, also known as persulfuric acid, peroxysulfuric acid is the inorganic compound with the formula H2SO5. It is a white solid. It is a component of Caro's acid, which is a solution of peroxymonosulfuric acid in sulfuric acid containing small amounts of water. Peroxymonosulfuric acid is a very strong oxidant (E0 = 2.51 V).
Structure
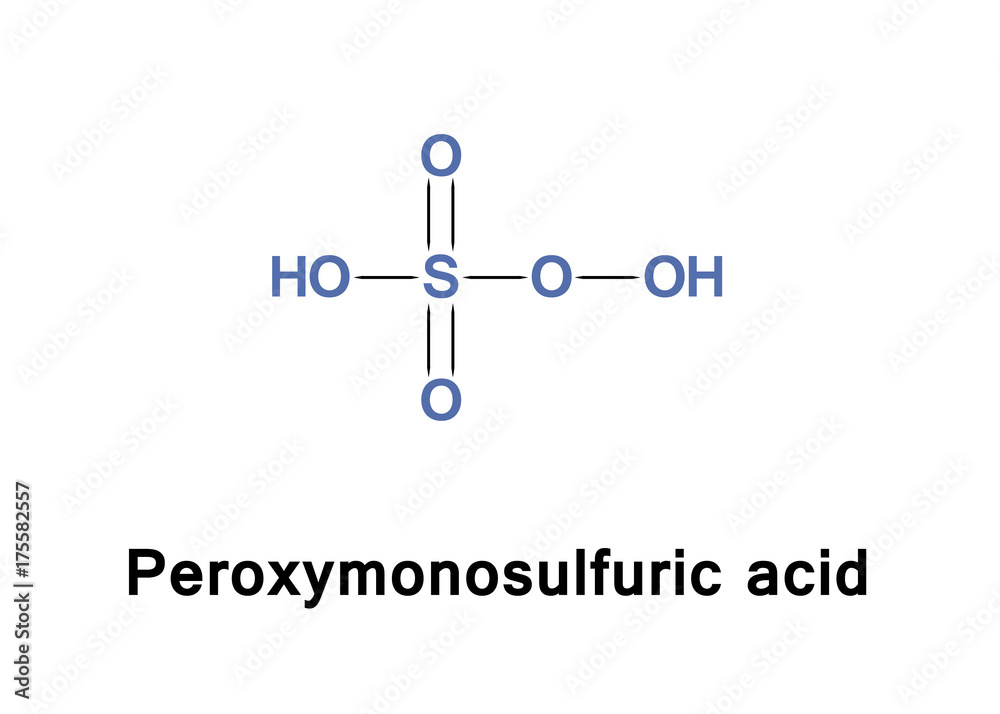
In peroxymonosulfuric acid, the S(VI) center adopts its characteristic tetrahedral geometry; the connectivity is indicated by the formula HO–O–S(O)2–OH. The S-O-H proton is more acidic.
History
The German chemist Heinrich Caro first reported investigations of mixtures of hydrogen peroxide and sulfuric acid.
Synthesis and production
One laboratory scale preparation of Caro's acid involves the combination of chlorosulfuric acid and hydrogen peroxide:
- H2O2 ClSO2OH ⇌ H2SO5 HCl
Patents include more than one reaction for preparation of Caro's acid, usually as an intermediate for the production of potassium monopersulfate (PMPS), a bleaching and oxidizing agent. One route employs the following reaction:
- H2O2 H2SO4 ⇌ H2SO5 H2O
This reaction is related to "piranha solution".
Uses in industry
H
2SO
5 and Caro's acid have been used for a variety of disinfectant and cleaning applications, e.g., swimming pool treatment and denture cleaning. It is used in gold mining to destroy the cyanide in the waste stream ("Tailings").
Alkali metal salts of H
2SO
5, especially oxone, are widely investigated.
Hazards
These peroxy acids can be explosive. Explosions have been reported at Brown University and Sun Oil. As with all strong oxidizing agents, peroxysulfuric acid is incompatible with organic compounds.
See also
- Peroxydisulfuric acid H
2S
2O
8, - Peroxomonosulfate
References